
Choose Year
RFID and NFC: Catalysts for Digital Product Passport Implementation
A Digital Product Passport (DPP) is a circular tool that uses a unique identifier to collect and share data across the value chain, enhancing transparency and promoting a more sustainable future. The core of the DPP is the data gathered throughout a product’s lifecycle, with the data carrier serving as the vital link between digital information and each stage of the value chain. RAIN RFID and NFC technologies offer significant advantages as data carriers, including providing unique identifier, high compatibility cross platforms, scalable and interoperable data collection, and easy access for both machines and value chain stakeholder groups. To effectively manage the vast amounts of data involved, the implementation of hybrid technologies makes more sense and is more resilient across the value chain. The DPP is too extensive for one technology alone.
Governed by the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR), the DPP will begin its phased rollout across various industries in 2027, marking a global shift that makes early preparation essential for companies.
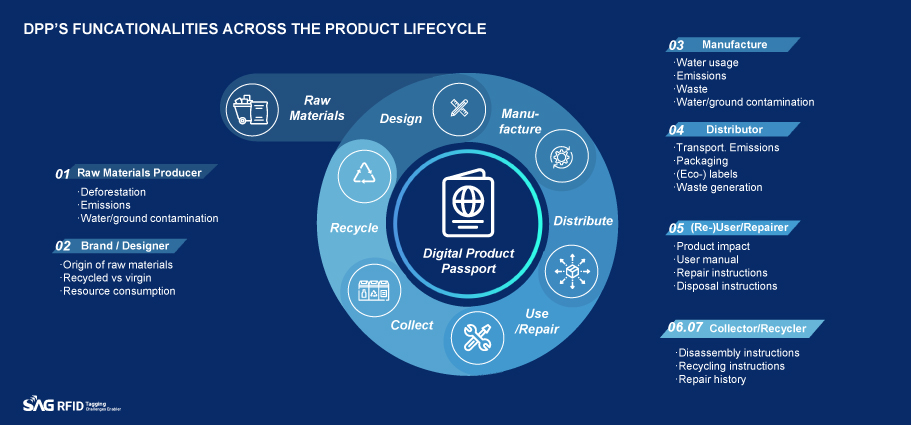
- Raw Materials: Deforestation, Emissions, Water/ground contamination
- Brand/ Designer: Origin of raw materials, Recycled v.s. Virgin, Resource consumption
- Manufacturer: Water usage, Emissions, Waste, Water/ground contamination
- Distributor: Transport emissions, Packaging, (Eco-) labels, Waste generation
- (Re-) User/ Repairer: Product impact, User manual, Repair instruction, Disposal instructions
- Collector/ Recycler: Disassembly instructions, Recycling instructions, Repair history
1. Electronics and ICT
2. Batteries and Vehicles
3. Textiles
4. Steel
5. Plastics
6. Furniture
7. Construction and buildings
8. Chemicals
The DPP is a powerful tool for advancing sustainability, and the EU is leading the charge as the first to implement large-scale actions for a circular economy. While the initial guidelines for the DPP are being established, we anticipate that the specifics will be refined over time. This pioneering effort underscores the EU's commitment to setting a global standard for environmental responsibility.
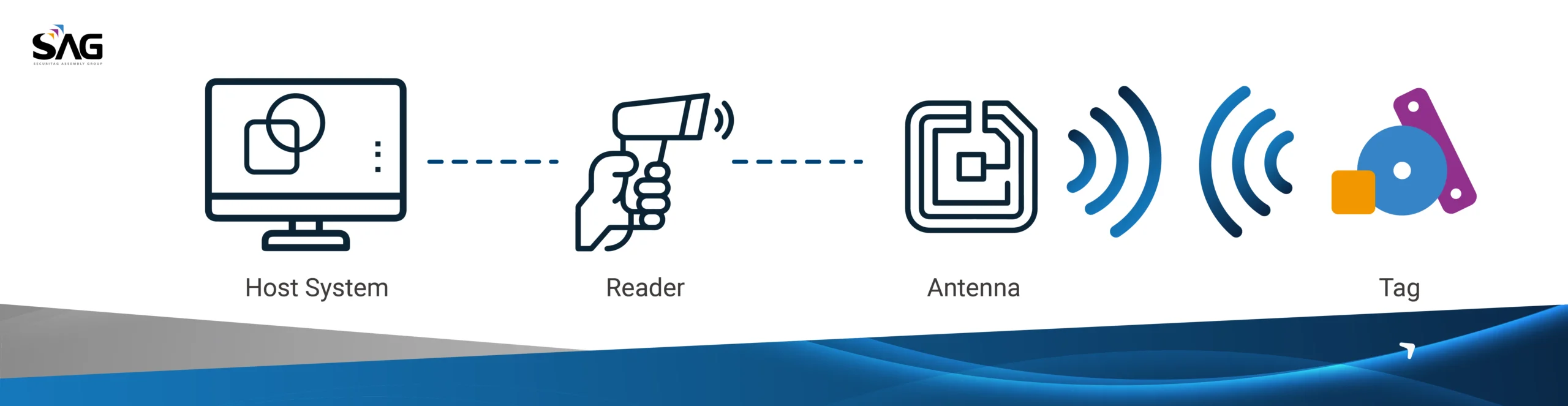
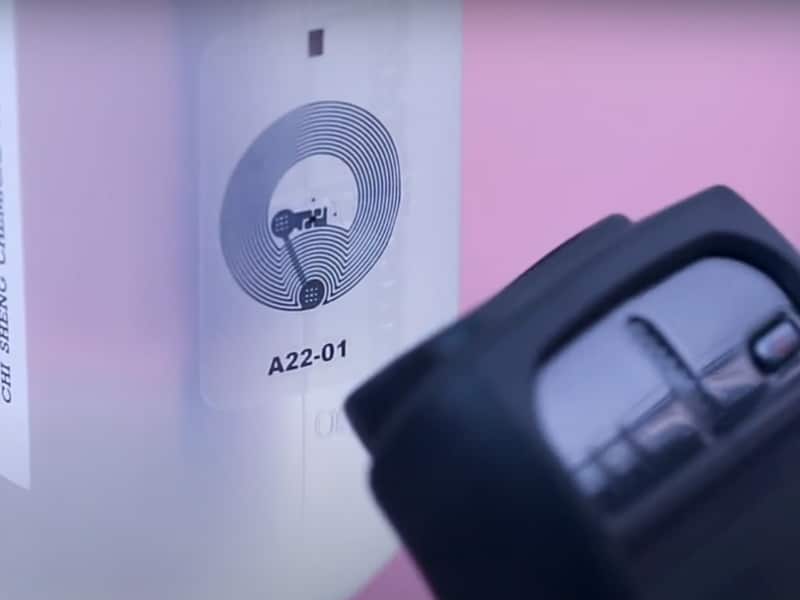
- Unique Identifier:
When using the DPP as a digital twin for a product, RFID and NFC tags provide a Unique Identification Number (UID) for every item, allowing it to be distinctly identified. These technologies also prevent counterfeiting and ensure product authenticity, a benefit widely leveraged in the luxury industry across their value chain. - Superior Compatibility:
RFID and NFC technologies offer superior compatibility across various platforms, adhering to the guidelines set by the EC. The data carriers comply with ISO/IEC standard 15459:2015, ensuring that all data is open, structured, and searchable. This compliance underscores the versatility and widespread applicability of RFID and NFC technologies in implementing DPP. - Advanced Scalability and Interoperability:
Data collection is central to the Digital Product Passport (DPP), with scalability and interoperability being critical for effective data management. RFID tags, which can be read automatically without requiring direct line-of-sight, enable quick and seamless data collection. When implementing the DPP for mass manufacturing, overall costs—including those for data carriers and infrastructure—can become a critical factor.
RAIN RFID has already been widely adopted in the retail market to support omnichannel capabilities, while NFC technology has proven valuable in luxury branding, enabling digital authentication and boosting consumer engagement through mobile devices. These advantages highlight how RFID technology serves as a catalyst for the implementation of the DPP. By ensuring scalability and interoperability, brands can efficiently manage data, reduce costs, and enhance overall process efficiency, ultimately driving compliance and innovation. - Strong Data Security and Digital Storage Capability:
Digital data storage is a key element of the DPP, providing a secure foundation for managing and accessing essential product data throughout its lifecycle. As data carriers, RFID and NFC technologies offer varying storage capacities, with RFID tags capable of holding up to 128 KB, while NFC tags range from 48 bytes to 1 MB, depending on the type. Additionally, these technologies support encryption, enhancing data protection by making it highly secure and significantly more challenging for unauthorized users to access or tamper with the information, unlike traditional plain text methods. - Easy Access:
Digital access capabilities and specific access rights for stakeholders throughout the value chain are key factors in the guidelines. RAIN RFID tags are highly effective for machine-reading and reading multiple items simultaneously from a long distance, benefiting the supply chain. Meanwhile, NFC tags can be easily read by most smartphones, enhancing engagement with end customers. - Long Durability:
The DPP, as a circular tool for enhancing sustainability, must be utilized from the raw material stage through to the product's End of Life (EOL). Maintaining normal functionality throughout the product's lifecycle is crucial, and RFID and NFC tags are designed to last at least 20 years under typical conditions. This longevity makes them highly durable and reliable for storing information throughout the entire lifecycle of a product.

- Inlay and Label: Commonly used in packaging and logistics for tracking goods, inventory management, and pharmaceutical packaging.
- Hard Tag: Ideal for asset management and industrial applications where durability is essential.
- Cards & Keyfob: Widely used for access control, identification, and cashless payment systems.
- Sensor Tag: Designed to monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and pressure. Sensor tags are ideal for cold chain management, environmental monitoring, and industrial process control.
- Enhanced Efficiency: RFID systems streamline operations by automating data collection and reducing manual errors. This leads to faster processes and improved productivity.
- Improved Visibility: With real-time tracking and data updates, RFID provides enhanced visibility not only into inventory but supply chain management . This allows for better decision-making and efficient resource utilization.
- Increased Security:RFID technology enhances security by enabling precise tracking of items and preventing unauthorized access. It provides an additional layer of protection for valuable assets and sensitive information.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement : NFC improves customer experience by providing transparent product information and personalized services, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Sustainability : By minimizing manual handling and transportation, RFID reduces waste and environmental impact. Additionally, lifecycle data collection offers businesses valuable insights that support and enhance green supply chain management.

Healthcare
Manual errors in healthcare cause significant losses every year. Implementing RFID tags ensures patient rights and improves process efficiency.

Pharmaceutical
Counterfeiting in pharmaceuticals lead to significant financial and safety issues. Implementing RFID tags helps track medications and ensures patient safety.

Manufacturing
Production inefficiencies and asset mismanagement can severely impact productivity and quality control. RFID tags optimize production processes and asset management.

Logistics and Supply Chain
Goods loss and inventory tracking errors are major challenges. RFID tags enhance tracking accuracy, optimize inventory, and increase supply chain visibility.

Product Authentication
Counterfeiting threatens product integrity and consumer trust. RFID tags provide reliable methods for verifying authenticity, protecting against counterfeiting, and enhancing customer engagement.

Acesses Control
Effective access control is essential in healthcare, commercial, residential, and entertainment sectors. RFID technology provides reliable methods for identification, verifying authenticity, and ensuring security.
Choosing the right RFID tag and product is essential to ensure optimal performance for your specific application. Before diving into the details, here are some shortcuts to help you figure it out quickly:
Product Selector: If you already have rough specifications, this tool helps you find the perfect product .
Contact Us: If you only have scenario or application ideas, our team are ready to provide assistance and guide you through the selection process.
The target application and use case ultimately determine the RFID tag or inlay requirements. Let’s start by considering the following questions:
Key factors to consider:
- Frequency:Ensure the chosen frequency of RFID tag is suitable for your application environment and read range requirements.
- Environment: Consider the environmental conditions the RFID tag will be exposed to, such as temperature, humidity, and potential interference.
- Read Range: Determine the required read range based on the application.
- Security: Evaluate the security features needed to protect the data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Storage Capacity: Consider the amount of data that needs to be stored on the tag.
Each of these factors is crucial for building an automated system, and even minor deviations can significantly reduce system accuracy.
Thus, the last but most important key factor is finding The Right Partner .
With over 20 years of experience, SAG have successfully assisted customers in overcoming their RFID tagging challenges across diverse applications in over than 200 countries.
As sustainability becomes a global priority, the circular economy is widely embraced as a solution. RFID tags, with their advanced tracking capabilities, play a crucial role as data carriers in fostering a greener world. Throughout the product lifecycle, RFID enhances sustainability at each stage:



